3D printer combined with 3D scanner
If you have a special object and want to reproduce it, would you model it in 3D? Ok, you shouldn't. This is the purpose of 3D scanning and 3D printing , working together "to help" create a copy!
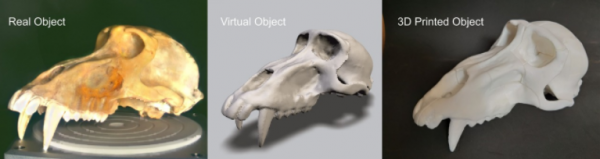
But what does a 3D scan object mean? What does 3D printing mean? In essence, these two technologies are mutually reversible. With one of them, you can convert a real object to a virtual object. On the Other hand, you use virtual objects to generate real objects.
Of course, if there is a machine that can do 3D scanning and 3D printing, that would be great. However, with the technology we now have, integrated scanning and printing is still limited to the 2D field.
Here, we introduce the process of 3D scanning and 3D printing, their differences, and the goals that can be achieved if they are used at the same time.
A 3D scanner is a device that collects physical data of an object or environment to create a digital model. This data can include volume, texture, and color.

There are two main types of 3D scanners: contact or non-contact.
Contact 3D scanning uses some type of arm, such as a robotic arm, with a probe. Once the object is in place, the probe contacts its surface to collect information about position and distance. When the detector scans an object, it maps the coordinates that ultimately make up the 3D model.
This technology is mainly used for manufacturing and is slower than other technologies. It also requires physical contact with the target object, which can be harmful.
Non-contact 3D scanning involves collecting radiation from a target object and using active or passive techniques:
Active scanners emit radiation, usually light or laser, and collect objects that are reflected from the surface of the object.
A passive scanner collects ambient radiation from another source and is reflected by the surface of the object.
Regardless of the technology used, non-contact scanners generate a grid of "seeing" of the received radiation based on their relative intensities.
A 3D printer is a device that generates real three-dimensional objects from a digital model.
When we talk about 3D printing, we usually refer to liquid light curing modeling, but there are other types of 3D printing, such as SLA and SLS:
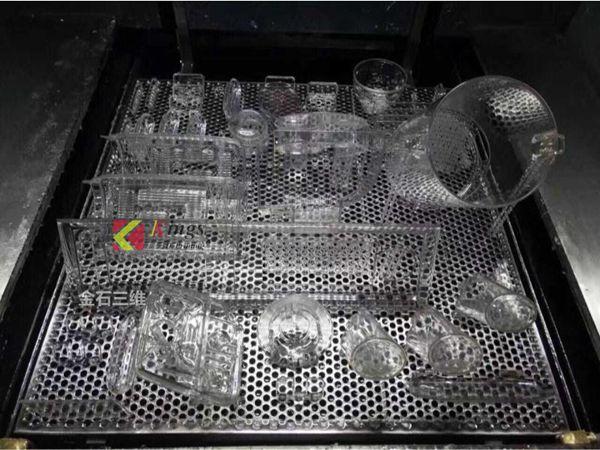

Fused deposition molding (FDM) melts the thermoplastic filaments with heated nozzles and extrudes the molten material, which is rapidly cooled to produce an object.
Stereolithography (SLA) uses UV light to convert liquid photopolymer plastics into solid objects.
Selective laser sintering (SLS) uses a laser to selectively melt the powder.
With all three techniques, the object is generated layer by layer. This means that a special software tool called a slicer must first convert the original 3D model into a command that the 3D printer can understand.
If you are interested in recreating an existing object, please provide a general procedure here:
Select the object to be 3D scanned and the 3D scanning technology. Please note that depending on the size of your model, you may be limited by what you scan.
3D scan object. You may need to reposition it to capture different perspectives. With simple objects, you may need at least three different locations. For more complex objects, you may need more than five. If you are using photogrammetry, check how many images the software needs. Please note that the more scans or photos you have, the better the 3D model.
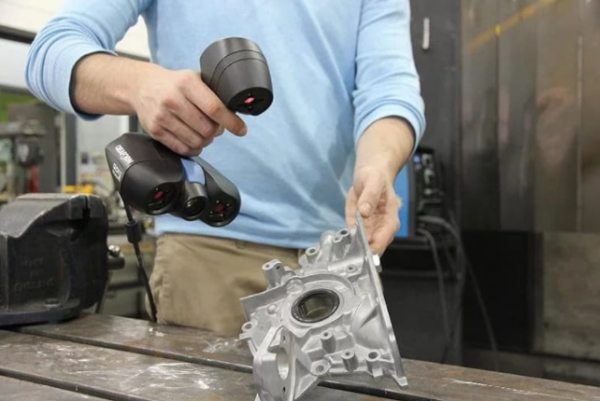

After the scan is complete, perform the necessary operations required for the corresponding software. Every scan or photo needs to be cleaned (supported, platform and background objects) and aligned. This is a very important step because all views must be properly aligned. If not, the final model will be distorted. When properly aligned, all overlapping meshes are merged into a single virtual object.
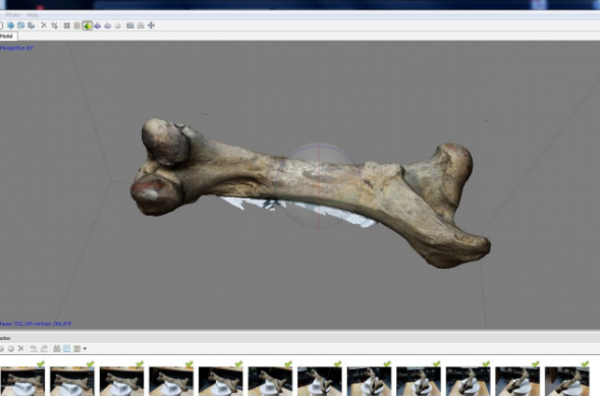
Export virtual objects as STL or OBJ files.
Import the STL or OBJ file into a slicer suitable for 3D printers and prepare to print. Once the necessary parameters are set, the slicer generates the necessary g code, which is the operation required to print the object one layer at a time.
Send the g code to the 3D printer and print the 3D copy.
Looking online, you'll find plenty of examples showing the practicality of combining 3D scanning with 3D printing. For example, in the medical field, when the patient's body is first scanned, it is easier to change the body part. Areas such as paleontology and archaeology have also benefited from making replicas of bones and artifacts.
Double Horizontal Wire Fencing is a robust form of fencing now often used in and around schools,colleges and commercial properties.It is usually galvanized and powder coated,the standard colors being green or black but can be powder coated in any color.Double Horizontal Wire Fence has the features of grid structure, beauty and practical, landscaping. In addition, Because of the double wire fencing features of easy transportation and installing without the limitations of special terrain. It is adjust to mountain, hillside and winding zones.
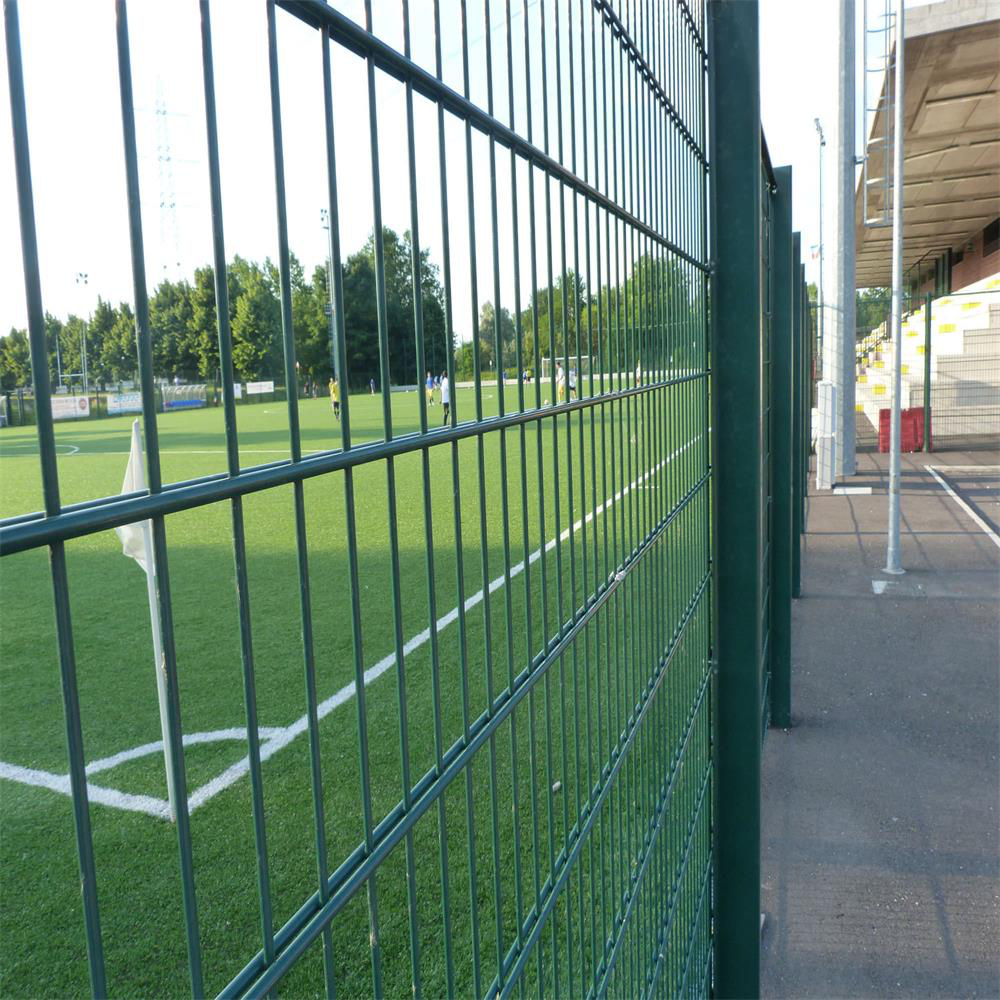

Double Horizontal Wire Fence,Horizontal Wire Fence,Galvanized Wire Fence,Welded Security Wire Fence
Hebei Giant Metal Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.hebeigiantmetal.com