Epoxy curing agent (a)
The curing agent refers to a class of substances that can convert a soluble and meltable linear structural polymer compound into an insoluble and infusible body structure. Epoxy adhesive is indispensable
The important component.
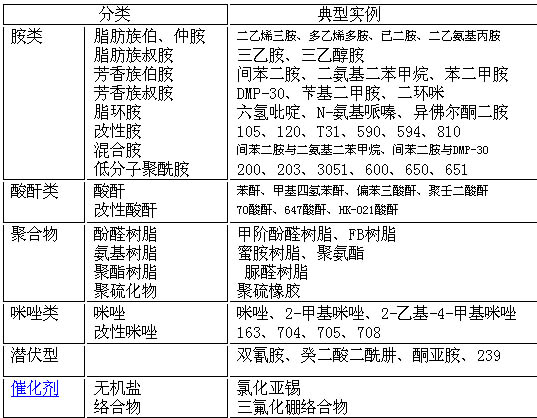
First, the classification of curing agents: habits can be divided into amines, anhydrides, carbazoles, polymers, latent, catalytic, etc., curing temperature can be divided into low temperature (-5 ~ 15), room temperature, secondary temperature (RT -50), medium temperature (50~100), high temperature (>100) curing agent.
Second, the amount of curing agent
The amount of curing agent is very important, too little amount of curing is not complete, the main properties of the adhesive curing poor; amount of too much, the adhesive layer brittleness increased. With reduced strength, residual curing agents can also damage the properties of the adhesive. The amount of curing agent must be appropriate, generally can be calculated and then finalized by experiment. The amount of curing agent generally refers to 100 parts of resin (phr).
Third, amine curing agent
The most variety, a wide range of uses. Curable at room temperature, excellent adhesion to most adherends. Cured chemicals are very good but amine curing agents are stronger
The water absorption and the ability to absorb CO2, the surface after curing is prone to whitening and foaming, the electrical properties are not good enough, and the bonding strength is not high.
When the epoxy resin is cured, primary (primary) amines and secondary (secondary) amines are the primary ones for epoxy based cleaning, and there is a strict quantitative relationship between amine groups and epoxy groups, ie 1
Only one epoxy group reacts with each active hydrogen, and the theoretical amount of primary and secondary amines can be calculated as follows
Wa = M / N × Ev = ae × Ev
Where Wa is the amount of epoxy curing agent per 100g (g)
M: Relative molecular mass of the curing agent
N: the total number of active hydrogen atoms in the curing agent;
Ev: epoxy value of epoxy resin
Ae : amine equivalent
For volatile amine curing agents, the actual amount added should be increased by 5% to 10% over the theoretical amount.
(A) Polyamine curing agent
(1) Diethylenetriamine Also known as diethylene triamine, diethylene triamine, referred to as DETA, DTA, with a relative molecular mass of 103.1. Colorless or light yellow oily liquid, with
Irritating ammonia.
(2) Triethylenetetramine Also known as triethylene tetraamine, triethylene tetraamine, triethylenediamine, abbreviated TETA, TTA, relative molecular mass 146.2 light yellow viscous liquid
Body, with ammonia smell.
(3) Tetraethylenepentamine Also known as tetraethylenepentamine, tetraethylenepentamine, triethylenediamine, tetraethylenepentamine. Referred to as TEPA, TPA, relative molecular mass 146.2.
Orange orange liquid has hygroscopicity.
(4), Polyethylene Polyamines Double called polyamine polyamines, poly ethylene polyamines, referred to as PEPA, the relative molecular mass of 300 ~ 500, up to 1100 ~ 2400, and even up to 5000.
Orange to tan liquid with ammonia smell.
(5) Dimethylaminopropylamine, also known as N,N-dimethyl-1,3-propanediamine, or DMAPA for short, is a colorless, transparent liquid with a relative molecular weight of 102.2.
(6) Diethylaminopropylamine Abbreviated as DEAPA, DEPA, molecular weight 130, colorless liquid.
(7) Dibutylaminopropylamine Abbreviated DBAPA.
(8) 1,6-Hexanediamine, also known as diamine, hexamethylenediamine, 1,6-diaminohexane, HAD, relative molecular mass 116.2 White flake, with ammonia odor.
(B) Dihydroxyphthalimide
The abbreviation BCPIS is made from the reaction of diaminodiphenylmethane (DDM) or diaminodiphenylether (DDE) with trimellitic anhydride (TMA).
Thermal new curing agent for curing E-51 epoxy resin.
(c) Tertiary amine curing agent
Tertiary amines are basic compounds and are anion-catalyzed type curing agents. Curing agent dosage changes the curing speed and properties of cured products, and the heat release during curing is also large. So one
It should not be used alone.
(1) Triethylamine Abbreviated as TEA Molecular Weight 101.2 Colorless light yellow transparent liquid with ammonia odor.
(2) Triethanolamine, abbreviated as TEOA, a colorless transparent viscous liquid with a relative molecular weight of 149.2. Slight ammonia smell.
(3), pyridine Abbreviated PRD relative molecular mass 79. 1 colorless liquid, with a special odor.
(4) 2-methylpyridine, also known as a-Picoline, abbreviated as MPRD Molecular Weight 93.1 A colorless liquid has an odor.
(5), Benzyldimethylamine dimethyl benzylamine referred to as BDMA relative molecular mass 135. 2, colorless to pale yellow liquid, ammonia smell.
Fluorescent Business Paste Special Paper is one of the high-end products of business paste special paper. There are five colors: pink, pink, orange, yellow and green. The production machine is 1760mm paper machine, the main weight is 75g, and the four specifications are 620mm. 770mm, 775mm and 927mm, products bright colors, uniform fiber tissue, smoothness, high height, high Tension is strong, impenetrable, can not afford hair powder, banner quantitative low, dust is very little. Fluorescent business paste paper is mainly used for messages, memos, classifications, notes, hints, marks, indexes, assignments, and other purposes. It is a simple and clear production and is a must for modern business, office, learning, and life. Our company produces a series of fluorescent products on good quality, some have replaced the import, become the domestic pillar of the products manufacturers. We can also provide special products to our customers according to our plan
Fluorescence Business Paste Special Paper
Fluorescence Business Paste Special Paper,Fluorescence Paper,Business Paste Special Paper Of Fluorescence,Pink Fluorescent Business Stickers
Mcc Meili Cloud Computing Industry Investment Co., Ltd. , http://www.mcc-offsetpaper.com